Example 2. A simply supported beam is loaded as shown in the diagram. Calculate the support reactions and draw the Bending Moment diagram, Shear Force Diagram, Axial Force Diagram. Determine the maximum bending moment.
Calculate the reactions at the supports of a beam
1. A beam is in equilibrium when it is stationary relative to an inertial reference frame. The following conditions are satisfied when a beam, acted upon by a system of forces and moments, is in equilibrium:
ΣFx = 0: HA + P1*cos(30) = 0
ΣMA = 0: The sum of the moments about a point A is zero:
- q1*4*(4/2) - P1*sin(30)*8 + RB*12 + M1 = 0
ΣMB = 0: The sum of the moments about a point B is zero:
- RA*12 + q1*4*(12 - 4/2) + P1*sin(30)*4 + M1 = 0
2. Solve this system of equations:
HA = - P1*cos(30) = - 20*0.8660 = -17.32 (kN)
Calculate reaction of roller support about point B:
RB = ( q1*4*(4/2) + P1*sin(30)*8 - M1) / 12 = ( 6*4*(4/2) + 20*sin(30)*8 - 42) / 12 = 7.17 (kN)
Calculate reaction of pin support about point A:
RA = ( q1*4*(12 - 4/2) + P1*sin(30)*4 + M1) / 12 = ( 6*4*(12 - 4/2) + 20*sin(30)*4 + 42) / 12 = 26.83 (kN)
3. The sum of the forces is zero: ΣFy = 0: RA - q1*4 - P1*sin(30) + RB = 26.83 - 6*4 - 20*sin(30) + 7.17 = 0
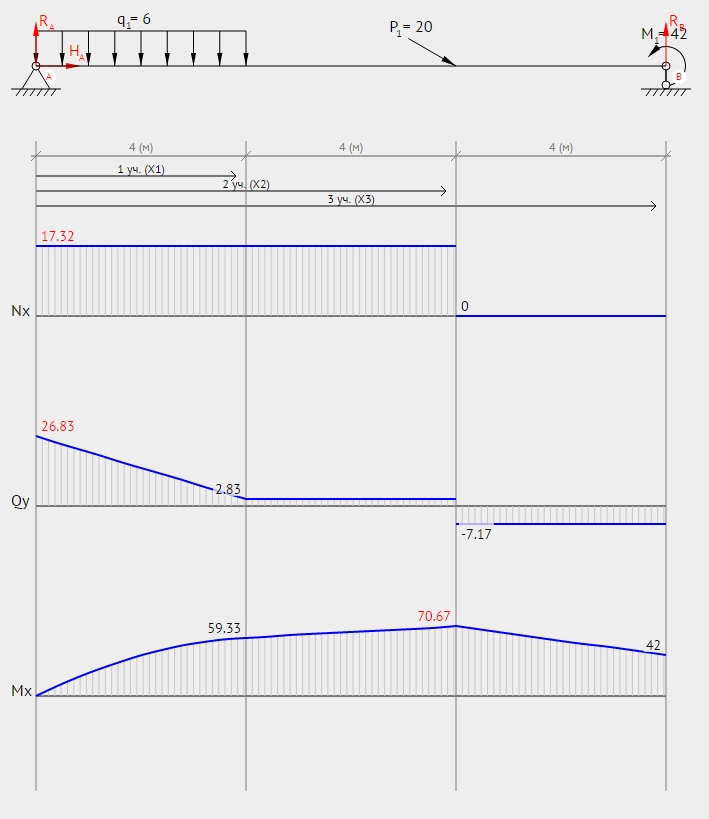
Draw diagrams for the beam
Determine the equations for the axial force (N):Second span of the beam: 4 ≤ x2 < 8
N(x1) = HA
N1(0) = 17.32 = 17.32 (kN)
N1(4) = 17.32 = 17.32 (kN)
Determine the equations for the shear force (Q):
Q(x1) = + RA - q1*(x1 - 0)
Q1(0) = + 26.83 - 6*(0 - 0) = 26.83 (kN)
Q1(4) = + 26.83 - 6*(4 - 0) = 2.83 (kN)
Determine the equations for the bending moment (M):
M(x1) = + RA*(x1) - q1*(x1)2/2
M1(0) = + 26.83*(0) - 6*(0 - 0)2/2 = 0 (kN*m)
M1(4) = + 26.83*(4) - 6*(4 - 0)2/2 = 59.33 (kN*m)
Determine the equations for the axial force (N):Third span of the beam: 8 ≤ x3 < 12
N(x2) = HA
N2(4) = 17.32 = 17.32 (kN)
N2(8) = 17.32 = 17.32 (kN)
Determine the equations for the shear force (Q):
Q(x2) = + RA - q1*(4 - 0)
Q2(4) = + 26.83 - 6*(4 - 0) = 2.83 (kN)
Q2(8) = + 26.83 - 6*(4 - 0) = 2.83 (kN)
Determine the equations for the bending moment (M):
M(x2) = + RA*(x2) - q1*(4 - 0)*[(x2 - 4) + (4 - 0)/2]
M2(4) = + 26.83*(4) - 6*4*(0 + 2) = 59.33 (kN*m)
M2(8) = + 26.83*(8) - 6*4*(4 + 2) = 70.67 (kN*m)
Determine the equations for the axial force (N):
N(x3) = HA - P1*cos(30)
N3(8) = 17.32 - 20*0.8660 = 0 (kN)
N3(12) = 17.32 - 20*0.8660 = 0 (kN)
Determine the equations for the shear force (Q):
Q(x3) = + RA - q1*(4 - 0) - P1*sin(30)
Q3(8) = + 26.83 - 6*(4 - 0) - 10.00*sin(30) = -7.17 (kN)
Q3(12) = + 26.83 - 6*(4 - 0) - 10.00*sin(30) = -7.17 (kN)
Determine the equations for the bending moment (M):
M(x3) = + RA*(x3) - q1*(4 - 0)*[(x3 - 4) + (4 - 0)/2] - P1*(x3 - 8)*sin(30)
M3(8) = + 26.83*(8) - 6*4*(4 + 2) - 20*(8 - 8)*sin(30) = 70.67 (kN*m)
M3(12) = + 26.83*(12) - 6*4*(8 + 2) - 20*(12 - 8)*sin(30) = 42 (kN*m)
Solved by BEAMGURU.COM