Example 4. Cantilever beam calculation carrying a triangular and a concentrated load
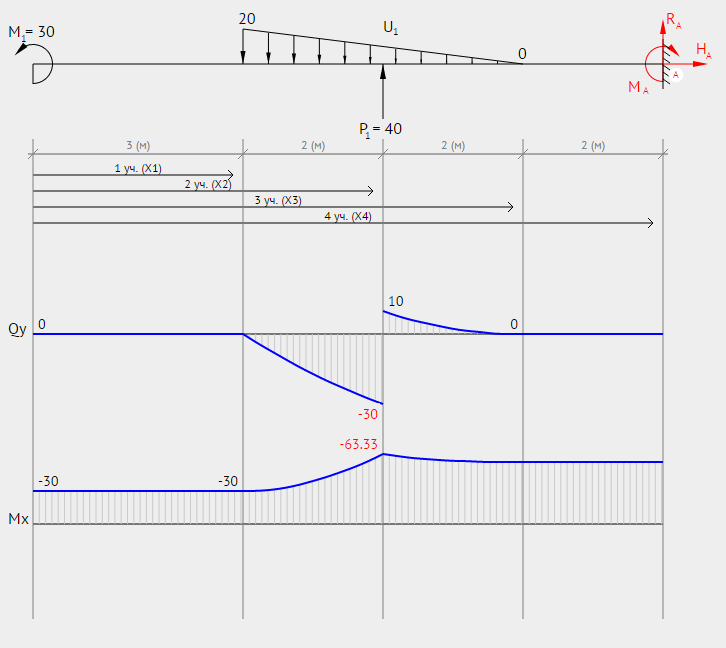
Calculate the reactions at the supports of a beam
A beam is in equilibrium when it is stationary relative to an inertial reference frame. The following conditions are satisfied when a beam, acted upon by a system of forces and moments, is in equilibrium:
1. The fixed support is located at point A (on the right). A fixed support will resist translation in all directions and rotation (moment) - HA, RA, MA.
2. The sum of the forces and moment about any point is zero: ΣFx = 0, ΣFy = 0, ΣMA = 0.
ΣFx = 0: HA = 0
ΣFy = 0: - (U1left *7)/2 - P1 + RA = 0;
ΣMA = 0: (U1left *7/2) * (9 - 8 + (2/3)*7) + 5*P1 + MA = 0;
3. Solve this system of equations:
HA = 0 (kN)
RA = (U1left *7)/2 + P1 = (30*7)/2 + 40 = 145.00 (kN)
MA = - (U1left *7/2) * (9 - 8 + (2/3)*7) - 5*P1 = - (U1left *7/2) * (9 - 8 + (2/3)*7) - 5*40 = -795.00 (kN*m)
4. Verification equation of equilibrium about the point A (on the left):
- (U1left *7/2) * (8 - (2/3)*7) - 4*P1 + 9*RA - MA = - (U1left *7/2) * (8 - (2/3)*7) - 4*40 + 9*145.00 - 795.00 = 0
Draw diagrams for the beam
Loads on this span is not specified.Second span of the beam: 1 ≤ x2 < 4
Determine the equations for the shear force (Q):Third span of the beam: 4 ≤ x3 < 8
Q(x2) = - ([(U1left - U1left *(8 - x)/7)*(x - 1)]/2 + U1left *(8 - x)/7*(x - 1))
Q2(1) = - ([(30 - 30*(8 - 1)/7)*(1 - 1)]/2 + 30*(8 - 1)/7*(1 - 1)) = 0 (kN)
Q2(4) = - ([(30 - 30*(8 - 4)/7)*(4 - 1)]/2 + 30*(8 - 4)/7*(4 - 1)) = -70.71 (kN)
Determine the equations for the bending moment (M):
M(x2) = + ([(U1left - U1left *(8 - x)/7)*(x - 1)]/2*(x - 1)*(2/3) + U1left *(8 - x)/7*(x - 1)*(x - 1)*(1/2))
M2(1) = - ([(30 - 30*(8 - 1)/7)*(1 - 1)]/2*(1 - 1)*(2/3) + 30*(8 - 1)/7*(1 - 1)*(1 - 1)*(1/2)) = 0 (kN*m)
M2(4) = + ([(30 - 30*(8 - 4)/7)*(4 - 1)]/2*(4 - 1)*(2/3) + 30*(8 - 4)/7*(4 - 1)*(4 - 1)*(1/2)) = -115.71 (kN*m)
Determine the equations for the shear force (Q):Fourth span of the beam: 8 ≤ x4 < 9
Q(x3) = - ([(U1left - U1left *(8 - x)/7)*(x - 1)]/2 + U1left *(8 - x)/7*(x - 1)) - P1
Q3(4) = - ([(30 - 30*(8 - 4)/7)*(4 - 1)]/2 + 30*(8 - 4)/7*(4 - 1)) - 40 = -110.71 (kN)
Q3(8) = - ([(30 - 30*(8 - 8)/7)*(8 - 1)]/2 + 30*(8 - 8)/7*(8 - 1)) - 40 = -145 (kN)
Determine the equations for the bending moment (M):
M(x3) = + ([(U1left - U1left *(8 - x)/7)*(x - 1)]/2*(x - 1)*(2/3) + U1left *(8 - x)/7*(x - 1)*(x - 1)*(1/2)) - P1*(x3 - 4)
M3(4) = + ([(30 - 30*(8 - 4)/7)*(4 - 1)]/2*(4 - 1)*(2/3) + 30*(8 - 4)/7*(4 - 1)*(4 - 1)*(1/2)) - 40*(4 - 4) = -115.71 (kN*m)
M3(8) = + ([(30 - 30*(8 - 8)/7)*(8 - 1)]/2*(8 - 1)*(2/3) + 30*(8 - 8)/7*(8 - 1)*(8 - 1)*(1/2)) - 40*(8 - 4) = -650 (kN*m)
Determine the equations for the shear force (Q):
Q(x4) = - (U1left *7)/2 - P1
Q4(8) = - ([(30 - 30*(8 - 8)/7)*(8 - 1)]/2 + 30*(8 - 8)/7*(8 - 1)) - 40 = -145 (kN)
Q4(9) = - (-30*7)/2 - 40 = -145 (kN)
Determine the equations for the bending moment (M):
M(x4) = + (U1left *7)/2*(x - 8 + (2/3)*7) - P1*(x4 - 4)
M4(8) = + ([(30 - 30*(8 - 8)/7)*(8 - 1)]/2*(8 - 1)*(2/3) + 30*(8 - 8)/7*(8 - 1)*(8 - 1)*(1/2)) - 40*(8 - 4) = -650 (kN*m)
M4(9) = + (-30*7)/2*(9 - 8 + (2/3)*7) - 40*(9 - 4) = -795 (kN*m)
Solved by BEAMGURU.COM